Indian Monsoons: South West Monsoons & North East Monsoons
Table of Contents
- Indian Monsoons |ITCZ|Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone
- Indian Monsoons Mechanism|Jet Stream Theory
- Indian Monsoons – Easterly Jet|Tibet|Somali Jet
- Indian Monsoons – South West|North East Monsoons <– You are Here
How Jet Streams affect Indian Monsoons? [Indian Monsoon Mechanism]
Summing up all the points from the previous posts.
- As the summer time approaches, there is increased solar heating of the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau.
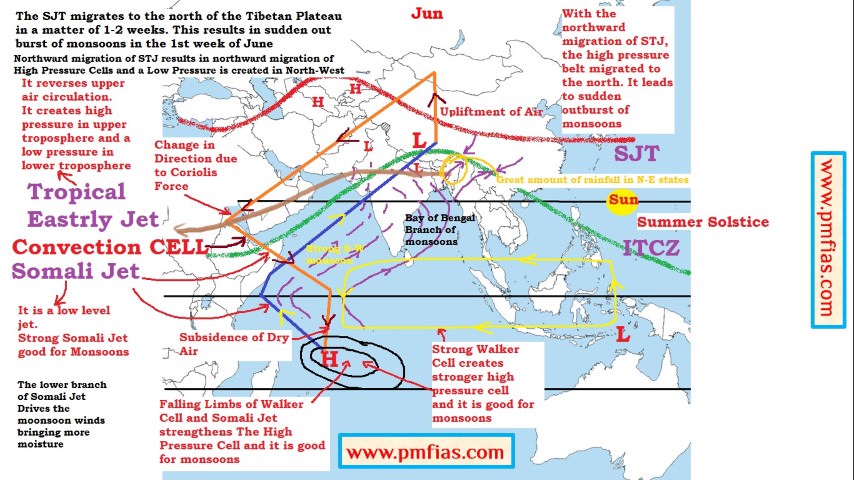
- In the peak summer months (25th of May – 10th of Jun), with the apparent northward movement of the sun, the southern branch of the SJT, which flows to the south of the Himalayas, shifts to the north of the Himalayas.
- When the sun’s position is about to reach the Tropic of Cancer (June), the SJT shifts to the north of the Tibetan Plateau (1st of Jun – 20th of June). The ITCZ is close to its peak position over the Tibetan Plateau.
- The altitude of the mountains initially disrupts the jet but once it has cleared the summits it is able to reform over central Asia.
- Its movement towards the north is one of the main features associated with the onset of the monsoon over India.
- With the northward shift of SJT, an Easterly Jet is formed over the Indian plains. It generally forms in the first week of June and lasts till late October.
- It can be traced in the upper troposphere right up to the west coast of Africa.
- The northward shift of SJT and ICTZ moves the subtropical high pressure belt to the north of the Tibetan Plateau and the Easterly Jet creates a low pressure region in the Indian plains (Easterly Jet creates anticyclonic conditions in upper troposphere).
- This low pressure in the northern plains coupled with the intense low of the Tibetan Plateau leads to the sudden onset of south-west monsoons (1st of Jun – 20th of June).
- The monsoon cell is situated between the Indian Ocean (North of Madagascar)(High Pressure Cell) and Tibetan plateau (Low Pressure Cell).
- In summer the sub-tropical easterly jet fluctuates between the plains region of India and peninsular India varying the intensity of rainfall from location to location.
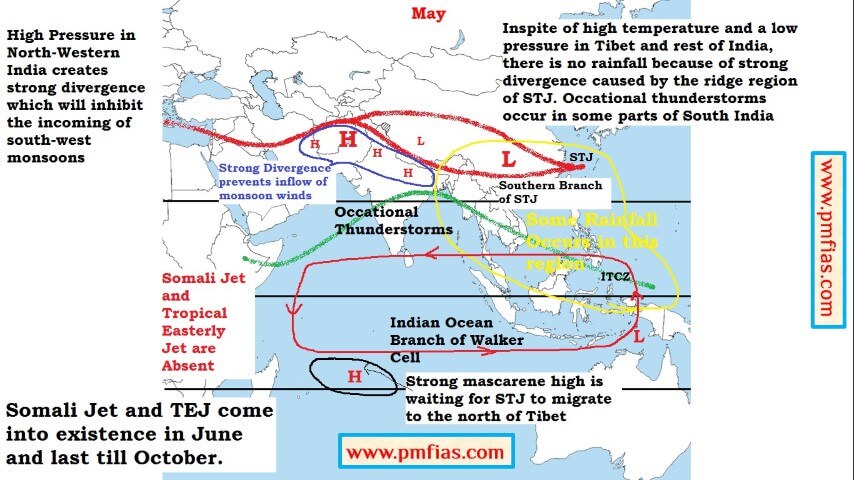
- During March to May, the building up of this cell is blocked by the STJ which tends to blow to the south of the Himalayas (Northwest India and Plains region are occupied by Subtropical High Pressure Belt. This high pressure belt undermines the influence of low pressure cell over Tibet).
- As long as the STJ is in this position the development of summer monsoons is inhibited (the high pressure belt stays over north India).
- With the STJ out of the way (high pressure belt migrates to the north of Tibet) the sub continental monsoon cell develops (Somali Jet) very quickly indeed, often in a matter of a few days.
- Warmth and moisture are fed into the cell by a lower level tropical jet stream which brings with it air masses laden with moisture from the Indian Ocean.
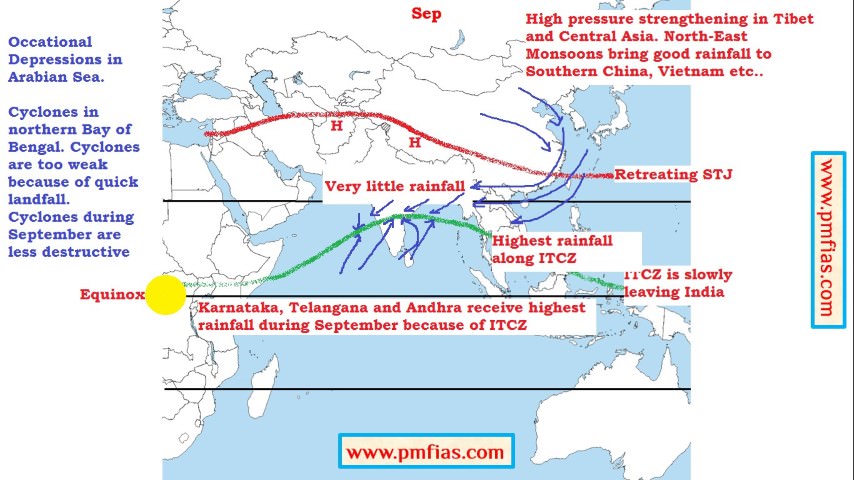
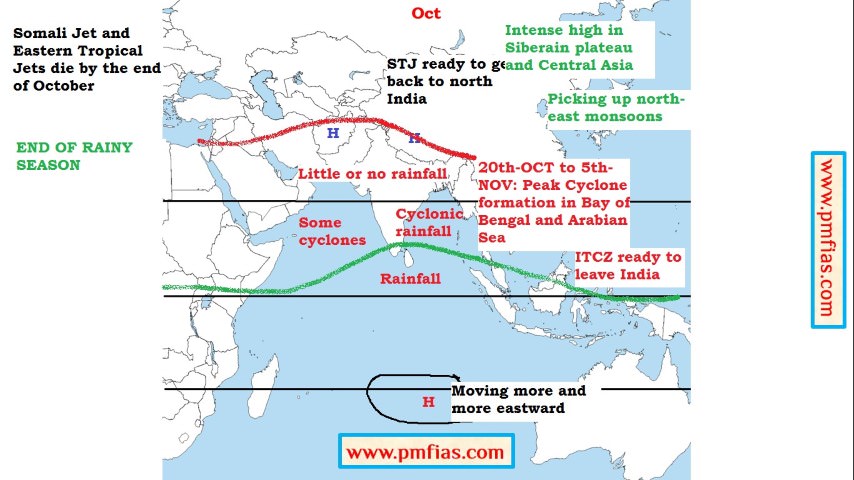
- The end of the monsoon season is brought about when the atmosphere over the Tibetan Plateau begins to cool (August – October), this enables the STJ to transition back across the Himalayas.
- With the southward shift of ITCZ, subtropical high pressure belt returns back to the Indian plains and the rainfall ceases.
- This leads to the formation of a anticyclonic winter monsoon cell typified by sinking air masses over India and relatively moisture free winds that blow seaward.
- This gives rise to relatively settled and dry weather over India during the winter months.
Indian Monsoons Seasonal Variations
Indian Monsoons in May – Dry Season
Indian Monsoons in June – Onset of Monsoons Jun 1st – June 1oth
Indian Monsoons in July – Monsoon winds reach North-West India

Indian Monsoons in August – Monsoons Retreat from North-West India

Indian Monsoons in September – Maximum Rainfall in parts of South India
Indian Monsoons in October – Retreating Monsoons – Cyclones in Late October
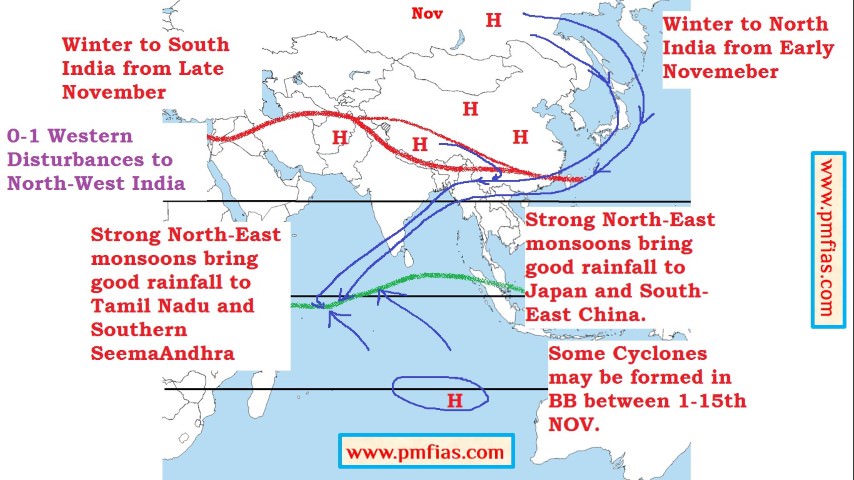
Indian Monsoons in November – North-East Monsoons – Peak Cyclone Season in early November
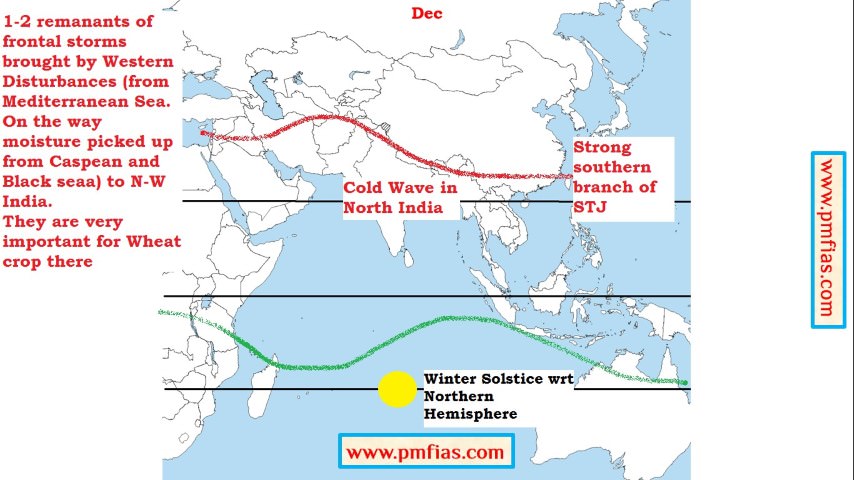
Indian Monsoons in December – Maximum Rainfall Month in Tamil Nadu and Southern Andhra Coast
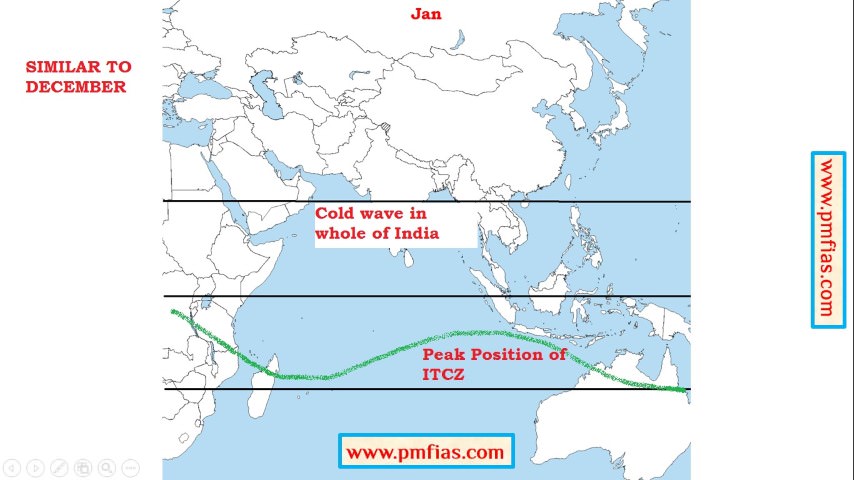
Indian Monsoons in January – North-East Monsoons weaken
Indian Monsoons in February – Dry Season Begins

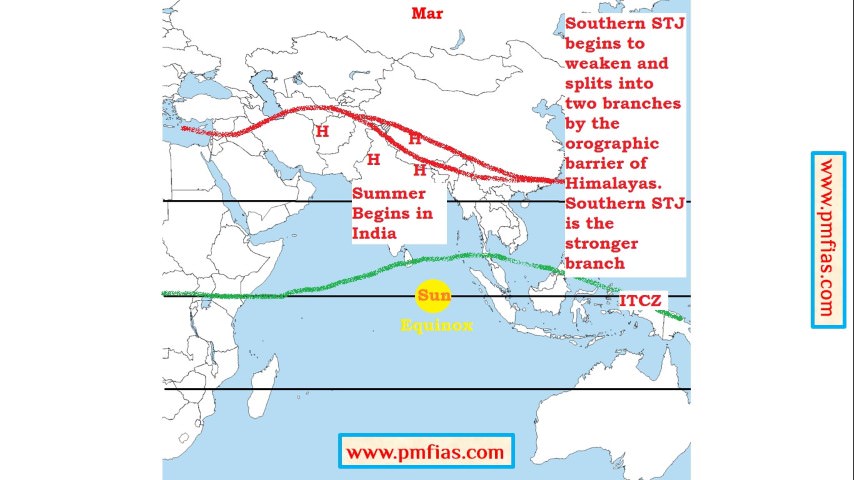
Indian Monsoons in March – Dry Season intensifies
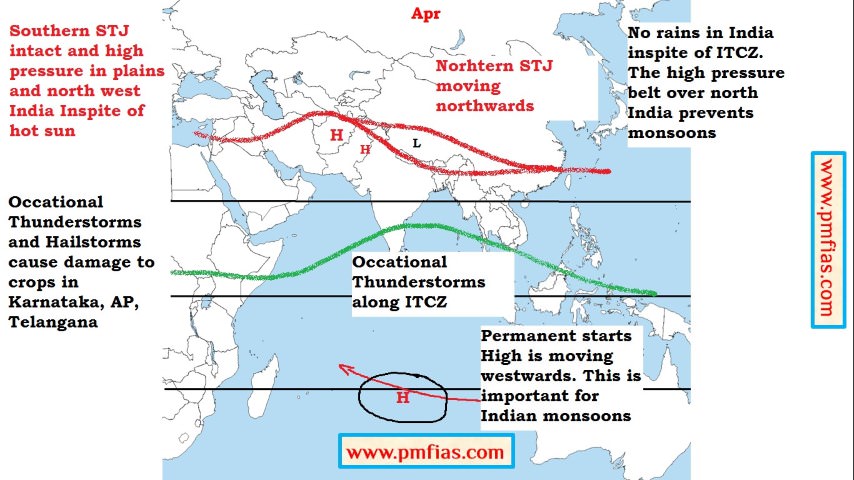
Indian Monsoons in April – Dry Season- Occasional Thunderstorms in South and Central India
Projects to understand monsoons
- First attempt was made during International India Ocean Expedition (HOE) from 1962 to 1965.
- It was organized jointly by the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU), Scientific Committee on Ocean Research (SCOR) and UNESCO with World Meteorological Organization (WMO) joining the meteorology programme.
ISMEX
- Two more experiments were conducted, jointly, by India and the former USSR in 1973 and 1977, with limited participation from other countries.
- These experiments are known as the Indo-Soviet Monsoon Experiment (ISMEX) and Monsoon-77 respectively.
MONEX
- Data collection effort was made under the aegis of MONEX-1979.
- It was organised jointly by many researching organizations and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) under their World Weather Watch (WWW) programme.
- It is so far the largest scientific effort made to understand monsoons.
- Details are not necessary. Remember the names. They can be asked in prelims. MONEX was asked in previous paper
s
No comments:
Post a Comment